The rapid ascent of Artificial Intelligence (AI) from a nascent technology to a core driver of economic strategy represents one of the most significant business transformations of the 21st century. Within the global landscape, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) has distinguished itself not merely as an adopter of AI but as a nation architecting its future around intelligent automation.
For enterprises operating within this dynamic environment, particularly in the commercial hub of Dubai, the deployment of AI-powered voice agents is transitioning from a competitive advantage to a strategic necessity. This shift is propelled by a unique confluence of top-down government vision, demonstrable market-driven returns, and the specific operational demands of the region’s key industries.
Understanding this strategic context is the foundational step for any organization contemplating an investment in conversational AI. It frames the decision not as a simple technology procurement, but as an alignment with a national economic trajectory. It’s a direct response to a market that is rapidly maturing and realizing tangible benefits from AI integration.
1.1 The Vision for an AI-Powered Economy: The UAE National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence 2031
The commercial landscape for AI in the UAE is fundamentally shaped by a clear and ambitious national agenda. The UAE National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence 2031, launched in 2017, is a cornerstone of the nation’s broader Centennial 2071 vision.
This strategy is not a passive policy document; it is an active blueprint designed to position the UAE as a global leader in AI by 2031. Its primary objective is to leverage AI as a catalyst for economic transformation, with a stated goal of generating AED 335 billion in economic growth.
This government-led vision creates a uniquely favorable ecosystem for businesses looking to invest in AI technologies like voice agents. The strategy outlines eight core objectives, including building a reputation as a global AI destination.
It also includes developing a fertile ecosystem for AI innovation, attracting and training top talent, and ensuring strong governance and regulation. The appointment of the world’s first Minister of State for Artificial Intelligence underscores the government’s commitment to this agenda.
The practical implications of this strategy are already visible. The “Smart Dubai” initiative, for instance, has successfully launched over 130 AI-driven services across critical public sectors such as transportation, governance, and safety.
Furthermore, the government is actively investing in human capital through large-scale skilling programs. A national initiative, in partnership with Microsoft, aims to train 100,000 government employees in AI, part of a broader commitment to train one million learners in AI skills by 2027.
These public sector deployments and investments serve a dual purpose: they directly improve government services and, crucially, they set a powerful precedent for the private sector.
By demonstrating the viability and benefits of AI at a national scale, the government de-risks investment for private enterprises and signals that AI adoption is a shared national priority.
This top-down “push” creates a market where investment in AI voice agents is not just a commercial decision but an alignment with the nation’s strategic direction. It promises a supportive regulatory environment and a growing pool of AI-literate talent.

1.2 Market Dynamics and Adoption Trends: A Data-Driven Overview
The UAE government’s strategic push for AI is met with an equally powerful “pull” from the market itself. Businesses are moving beyond experimentation to achieve significant, measurable results.
The narrative of AI adoption in the UAE is not one of future potential but of current, tangible returns, making a compelling quantitative case for investment.
According to the IBM Global AI Adoption Index 2023, 42% of businesses in the UAE are already actively using AI in their operations, a figure that underscores a mature adoption cycle.
Furthermore, 65% of these organizations report having significantly accelerated their AI rollout over the past 24 months, indicating a market that is gaining momentum rapidly. This acceleration is fueled by demonstrable success.
A separate, more recent IBM study reveals that 77% of UAE enterprises have achieved significant operational productivity improvements using AI. This figure stands well above the EMEA regional average of 66%.
The financial returns on these investments are not a distant prospect but an imminent reality for many. The same study found that over 44% of UAE businesses expect to achieve a return on investment (ROI) from their AI initiatives within the next 12 months.
This expectation is spread across key business metrics, including cost reduction (40%), time savings (49%), increased revenue (41%), and improved employee satisfaction (47%).
The rapid realization of ROI creates a powerful self-reinforcing cycle: government vision encourages initial investment, successful early adopters demonstrate tangible and swift returns, which in turn validates the national strategy and encourages broader, more ambitious market adoption.
This data reveals a crucial shift in how AI is being leveraged. The focus is moving beyond simple cost-cutting towards strategic value creation. Senior leaders report that the time saved through AI-driven productivity is being reinvested in higher-value activities.
Employees are spending more time developing new ideas, pursuing upskilling and professional development, and engaging in strategic decision-making and creative work.
Most tellingly, nearly a quarter (26%) of leaders who reported significant productivity gains credit AI with fundamentally changing their business models.
This indicates that AI, including sophisticated voice agents, is not merely being used to automate existing processes but to redesign them, creating new efficiencies and value streams.
For a business in Dubai, this means the competitive benchmark is no longer just about reducing call wait times. It’s about using conversational AI to free up human capital for innovation and strategic growth.
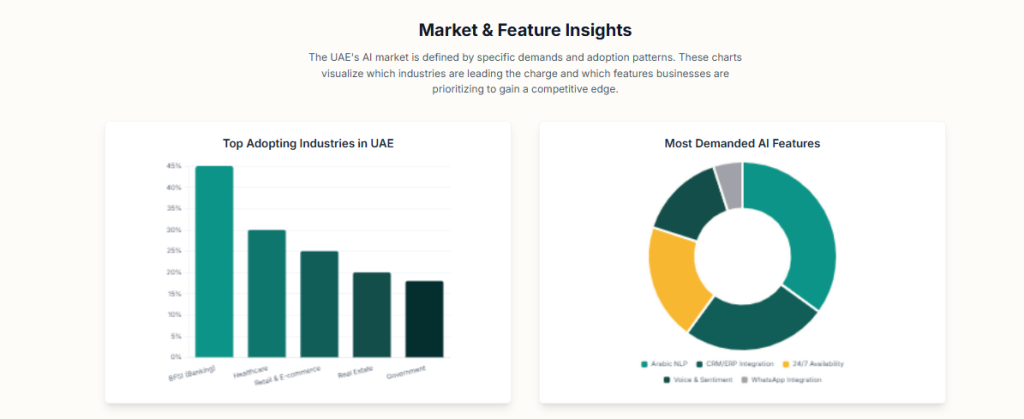
1.3 Key Industry Verticals in Dubai: Use Cases and Challenges
The strategic value of AI voice agents becomes most apparent when examined through the lens of Dubai’s key economic sectors. The technology’s applications are not generic; they are tailored to solve specific operational challenges and unlock unique opportunities within each industry.
Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI): The BFSI sector in Dubai is a prime candidate for AI voice automation. This is driven by high call volumes, stringent security requirements, and the need for 24/7 customer support.
One of the UAE’s leading banks, Emirates NBD, provides a powerful case study with its launch of EVA (Emirates Virtual Assistant). This conversational AI helps customers with tasks like checking balances and finding branches.
This led to a 35% drop in response time compared to traditional phone support and a 20% reduction in call center volume. Providers like SAN Softwares and Konvergense specifically target this sector, offering AI virtual assistants to handle bank inquiries and process transactions.
Konvergense is developing sophisticated solutions like voice biometrics for secure authentication in Dubai’s financial institutions. Nxtaa Technologies also offers secure, PCI DSS-compliant contact center solutions for banks and fintech firms.
Retail and E-commerce: For Dubai’s booming retail sector, AI voice agents address the challenge of managing massive customer interaction volumes, especially during peak seasons and sales events.
Noon, a leading UAE-based online retailer, uses AI chatbots to handle a wide range of queries from order status to product information and automated refunds. This allows them to scale support without proportionally increasing human staff.
Providers like Cezcon Solutions and Nxtaa Technologies cater to this industry, offering solutions for order integration, returns processing, and inventory lookup. The goal is to provide instant, accurate support to a customer base that expects immediate gratification.
Healthcare: In healthcare, AI voice agents are transforming the patient experience by streamlining administrative processes that are often frustrating bottlenecks.
Use cases include automated appointment booking, patient reminders, and handling initial inquiries. This reduces wait times and frees up clinical staff to focus on patient care.
Providers like SAN Softwares, Callab.ai, and Nxtaa Technologies offer tailored solutions for this vertical, with Nxtaa emphasizing HIPAA compliance to ensure patient privacy.
The UAE’s broader push for AI in healthcare, including national-scale data platforms like Malaffi and NABIDH, creates a rich environment for these technologies to thrive. AI is already being used to accelerate diagnostics and automate administrative tasks, leading to faster appointment booking and reduced workloads.
Real Estate: The dynamic real estate market in Dubai benefits from AI voice agents that can qualify leads around the clock, schedule property viewings, and provide instant information on listings.
This ensures that no potential buyer or tenant inquiry is missed, regardless of when it is made. Callab.ai and SAN Softwares both highlight real estate as a key industry, offering smart AI agents to manage property-related phone calls and streamline tenant management.
Telecommunications and Hospitality: Telecom giant Etisalat uses its AI bot, “Eya,” which is fluent in both Arabic and English, to resolve a high volume of routine customer issues.
This strategy has resulted in 70% of queries being resolved without human involvement in the first three months. This allows human agents to focus on more complex problems.
Similarly, in the hospitality sector, which is central to Dubai’s economy, Konvergense has developed AI voice bots to automate inbound calls, addressing the unique challenges of a high-turnover, 24/7 industry.
These industry-specific applications demonstrate that the adoption of AI voice agents is not a speculative trend. It is a proven strategy for solving real-world business problems in Dubai’s most critical economic sectors.

Part 2: The Provider Landscape for AI Voice Agents
The market for AI voice agent solutions in the UAE is a complex and diverse ecosystem. It comprises a mix of highly specialized regional players, global technology giants, local system integrators, and bespoke development agencies.
For a Dubai-based enterprise, navigating this landscape requires a clear understanding of the different types of providers and their core value propositions.
The choice of a partner is not merely a technical decision but a strategic one. It reflects the organization’s desired level of control, speed to market, and approach to acquiring and managing AI capabilities.
The selection process can be framed as a choice between three primary models: “Buy” a ready-made platform, “Build” a custom solution, or “Integrate” AI capabilities as part of a broader digital transformation partnership.
2.1 A Framework for Vendor Categorization
To bring clarity to the provider landscape, it is useful to segment the market into distinct categories based on their business models, core competencies, and geographic focus. This framework allows a potential buyer to quickly identify the class of provider that best aligns with their strategic objectives.
Specialized AI Voice Platforms (MENA-Focused): These are technology companies whose core product is a sophisticated conversational AI platform. They often have a specific and deep focus on the linguistic and cultural nuances of the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region.
They represent the quintessential “Buy” option, offering a feature-rich, scalable Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solution. Their primary differentiator is often a superior, ground-up understanding of Arabic dialects.
Global Omnichannel Conversational AI Platforms: This category includes major international players who offer comprehensive, enterprise-grade platforms for managing customer interactions across all channels (voice, chat, email, social media).
While they possess immense technical depth and broad integration capabilities, their “local presence” may be primarily focused on sales and support rather than region-specific R&D. They offer a powerful “Buy” option for large enterprises seeking a single, unified platform for global operations.
Local/Regional IT Integrators & Solution Providers: These are established UAE-based companies that offer AI voice agent development as part of a wider portfolio of IT services. This may include contact center solutions, CRM implementation, and digital marketing.
They represent the “Integrate” model, positioning themselves as a single strategic partner for a company’s broader digital journey. Their value lies in their deep, long-standing knowledge of the local business environment and their ability to provide end-to-end solutions.
Custom Development & Consulting Agencies: This group consists of software development firms and consultancies that specialize in building bespoke AI solutions from the ground up. They are the “Build” option, ideal for companies with highly unique requirements that cannot be met by off-the-shelf platforms.
They offer maximum flexibility and customization but typically involve longer development timelines and higher initial investment.
Infrastructure & API Providers (CPaaS): These are the foundational technology providers, often referred to as Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS) companies. They offer the building blocks—such as voice APIs, speech-to-text services, and telephony infrastructure—that other developers use to build their own voice agent solutions.
While not end-user solution providers themselves, they are a critical part of the ecosystem. They represent the most fundamental “Build” approach for organizations with deep in-house technical expertise.
2.2 In-Depth Provider Profiles
An analysis of the key players within each category reveals their distinct strengths, target markets, and strategic positioning.
Profile 1: Maqsam (Specialized MENA-Focused Platform) Core Proposition: Maqsam positions itself as the leading “Arabic-first” AI-powered contact center solution specifically designed for the MENA region. The company’s entire philosophy and technological development are centered on solving the unique challenges of the Arabic language.
Their most significant differentiator is a proprietary Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) engine trained natively on Arabic. They claim it outperforms global tech giants like Meta, Google, and Microsoft in accuracy for regional dialects. This focus on deep linguistic and cultural understanding makes them a compelling choice for businesses where flawless Arabic communication is a primary requirement.
Offerings: Maqsam provides a comprehensive suite of tools including an AI Agent capable of handling full conversations, qualifying leads, and offering smart escalation to human agents. The platform also includes broader customer service software features like an IVR builder, sentiment analysis, call summaries, and the provision of local phone numbers in hundreds of cities.
Integrations: The platform offers native integrations with leading CRM and helpdesk solutions, including Zendesk, Zoho, Intercom, Pipedrive, Salesloft, and Freshdesk, enabling seamless workflow automation.
Clients/Credibility: Maqsam is trusted by over 1,400 companies and features testimonials from regional businesses such as Hafla, Trukker, and Ingot Brokers. The company’s credibility is further bolstered by recognition from Deloitte’s Technology Fast 50 list and positive G2 customer reviews.
Profile 2: Callab.ai (Specialized MENA-Focused Platform) Core Proposition: Similar to Maqsam, Callab.ai focuses on providing AI call management solutions with a deep emphasis on authentic, human-like conversations tailored for the MENA market.
Their value proposition centers on achieving “cultural intelligence you can hear.” They have a specific capability to understand and speak a variety of Arabic dialects, which they argue is key to building trust and engagement.
Offerings: Callab.ai’s platform includes AI agents for both inbound and outbound calls, a “Knowledge Bank” that allows the AI to reference internal documents (PDFs, websites) during calls, and comprehensive post-call analysis with sentiment tagging.
It also features intelligent call transfer and routing, structured data extraction from conversations, and a batch calling feature for large-scale outreach campaigns.
Integrations: The company states that its agents integrate seamlessly with preferred CRMs, but a detailed, public list of native integrations is not readily available, requiring direct inquiry for specifics.
Clients/Credibility: Callab.ai’s website highlights partnerships with “visionary clients” but does not provide specific, named case studies from the UAE in the available materials.
Their strategy appears to involve establishing thought leadership through a blog. This content specifically addresses the UAE market, such as guides for upgrading local call centers and discussions on the nuances of voice AI in the region.
Profile 3: Yellow.ai (Global Omnichannel Platform) Core Proposition: Yellow.ai is a leading global, enterprise-grade conversational AI platform. They have moved towards positioning their solution as an “Agentic AI” platform, capable of automating complex interactions for both customer experience (CX) and employee experience (EX).
Their platform is built on a multi-LLM architecture, giving it flexibility and power, and it supports interactions across numerous channels, including voice, chat, and email.
UAE Presence & Clients: Yellow.ai demonstrates a strong commitment to the region with a physical office in the UAE. This is not just a token presence; they serve a portfolio of major Middle Eastern brands, including Carrefour, Kuwait Food Company (Americana), and Choithrams.
This provides significant credibility and demonstrates their platform’s suitability for large-scale regional enterprises.
Offerings: The platform’s key features include advanced voice automation, AI chatbots, a proprietary DynamicNLP™ engine with a claimed 97% intent accuracy, omnichannel orchestration that maintains context across channels, and robust analytics.
They have successfully deployed after-hours voice AI solutions for clients, automating routine queries and achieving significant cost savings.
Credibility: Yellow.ai’s global standing is validated by its recognition as a Challenger in the Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for Enterprise Conversational AI Platforms.
The company serves over 1,300 enterprises in more than 85 countries. It boasts a vast library of over 150 pre-built enterprise integrations with systems like Salesforce, Zendesk, Genesys, and HubSpot.
Profile 4: Konvergense (Local IT Integrator & Solution Provider) Core Proposition: Konvergense is a Dubai-based digital agency with a long history in the region, founded in 2008. With over 17 years of experience in the GCC market, their primary value proposition is deep, localized market knowledge.
They offer custom AI Agent and Chatbot development as part of a full suite of digital services. They position themselves as a strategic partner for businesses’ entire digital transformation journey.
Offerings: Their AI voice solutions are comprehensive, featuring multi-lingual AI Voice Assistants fluent in Arabic, English, and over 30 other languages.
They offer advanced capabilities such as conversational IVR, voice biometrics for security, and omnichannel integration across voice, WhatsApp, and SMS. They claim their infrastructure is robust, serving millions of interactions monthly and capable of scaling from 50 to 50,000 calls per day.
Clients/Credibility: Konvergense caters to a diverse clientele in the UAE, ranging from local SMEs to Fortune 500 companies across key sectors like healthcare, finance, retail, and real estate. They boast a high 95% client retention rate, suggesting strong, long-term partnerships.
Profile 5: Nxtaa Technologies (Local IT Integrator & Solution Provider) Core Proposition: Nxtaa Technologies is another Dubai-based provider that offers an integrated “AI-Powered Business Communication Hub”.
Their model combines AI solutions (voice agents and chatbots) with their own contact center platform, WhatsApp Business API integration, and digital marketing services. This positions them as a one-stop-shop for companies looking to unify their customer communication and marketing technology stack.
Offerings: Their AI voice agents are designed for phone support and are equipped with speech recognition and natural conversation abilities. The solution is tightly integrated with their contact center platform, enabling features like intelligent routing and real-time sentiment analysis.
They support over 15 languages and emphasize enterprise-grade security.
Clients/Credibility: Nxtaa claims to serve over 300 brands across various industries within the UAE, demonstrating a significant local footprint. Their client base spans financial services, healthcare, and e-commerce, for which they offer tailored, compliance-aware solutions (e.g., HIPAA, PCI DSS).
Profile 6: SAN Softwares (Local IT Integrator & Solution Provider) Core Proposition: SAN Softwares is a UAE-based company providing a broad range of business software solutions, among which is the “SanIVR Bot,” an AI-enabled voice bot system.
They offer an accessible entry point into AI voice automation, particularly for businesses already using their other software products.
Offerings: Their AI Voice Agent is designed to handle both outbound and inbound calls for use cases such as appointment booking, lead qualification, document verification, and customer feedback collection.
The platform supports multiple languages, including Arabic, and emphasizes seamless integration with CRM systems.
Clients/Credibility: The company explicitly markets its AI voice solutions to businesses in the UAE and across the broader Middle East, indicating a clear regional focus.
Profile 7: Other Notable Providers (Custom Development & Infrastructure) The UAE market is also served by a number of other firms offering more specialized or foundational services:
Custom Development Agencies: Companies like Cezcon Solutions, Infomates Technologies, and AGAN Cyber Security provide custom AI chatbot and virtual assistant development services. They work closely with clients to build tailor-made solutions that align with specific business goals and brand identities.
Voice Solution Specialists: Purple Rock, a Dubai-based IT company, offers a range of “voice solutions,” including voice bot and voice AI solutions, often built upon technologies like VoIP and PBX systems. They focus on integrating these solutions with existing CRM and helpdesk software.
Infrastructure Providers (CPaaS): At the foundational level, companies like Plivo provide the essential APIs and infrastructure for voice communication in the UAE. They offer per-minute pricing for local and mobile calls, as well as services like Automatic Speech Recognition and Text-to-Speech.
While they do not sell a finished AI agent product, their services likely power many of the custom solutions built by local development agencies.
This varied landscape underscores a critical point for buyers: the definition of a “local provider” is nuanced. It ranges from global giants with a strong regional sales office (Yellow.ai) to long-standing Dubai-based agencies with deep market experience (Konvergense).
It also includes specialized tech startups with a laser focus on regional linguistic challenges (Maqsam, Callab.ai). The most valuable form of “local presence” is not a physical address but demonstrated expertise.
This expertise is shown through relevant regional case studies, a deep understanding of local dialects, and solutions that cater to regional compliance and business culture.
Part 3: Comparative Analysis of Core Voice Agent Capabilities
A thorough evaluation of AI voice agent providers requires moving beyond marketing claims to a systematic comparison of their core technological capabilities.
For a business operating in Dubai, the most critical dimensions of comparison are the sophistication of the conversational AI, the depth of Arabic language support, the breadth of enterprise integrations, and the robustness of operational features like security and analytics.
An analysis across these vectors reveals significant differentiation among providers and provides a clear basis for shortlisting potential partners.
3.1 Conversational Intelligence and NLP
The intelligence of a voice agent is determined by its underlying Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Natural Language Understanding (NLU) engine. The ability to handle the complexities of human conversation is what separates a basic Interactive Voice Response (IVR) system from a truly effective AI agent.
Leading platforms demonstrate sophistication in several key areas. Maqsam, for example, explicitly highlights its agent’s ability to handle interruptions “like a pro.” This is a crucial feature for natural-feeling conversations, as users do not always wait for a prompt before speaking.
Callab.ai and Konvergense emphasize their agents’ ability to understand context and remember previous interactions, allowing for more coherent and personalized dialogues.
Sentiment analysis is another key feature of advanced conversational intelligence. It enables the agent to detect a user’s emotional state (e.g., frustration, satisfaction) and adapt its responses or escalate to a human agent accordingly.
This capability is offered by several providers, including Maqsam, Callab.ai (which provides sentiment-tagging in its post-call analysis), Nxtaa Technologies, and Awaz.ai.
The architectural foundation of the AI engine is also a point of differentiation. Yellow.ai leverages a multi-LLM (Large Language Model) architecture, utilizing over 15 cutting-edge models to enhance speed and accuracy.
This approach allows them to select the best model for a specific task, offering flexibility and power. In contrast, providers like Maqsam are developing their own proprietary LLM, specifically trained on regional data to optimize for local language and context. This represents a different but equally valid strategy focused on specialization.

3.2 The Arabic Language Advantage: A Critical Differentiator
For any business serving the diverse population of Dubai and the wider UAE, the quality of Arabic language support is arguably the single most important technical differentiator. Basic support for Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) is table stakes; true value lies in the ability to understand and interact in the various spoken dialects of the region.
This is where MENA-focused specialists have a distinct advantage. Maqsam has built its entire brand around being “Arabic-first”. Their AI agent is trained to understand major Arabic dialects, including GCC (Khaleeji), Levantine, and Egyptian, and speaks in a neutral, regionally understandable tone.
Their confidence in this area is backed by internal benchmarks showing their ASR technology surpasses that of global leaders for Arabic transcription. They also capably handle “Arabizi” or mixed-language queries that blend Arabic and English, a common conversational pattern in the region.
Callab.ai shares this deep focus on regional linguistics. They emphasize that their AI understands and speaks a variety of Arabic dialects, which they see as essential for achieving authentic connection and building trust with users across the MENA region.
Their technology is designed to understand cultural subtleties and regional phrases, adapting to the user rather than forcing the user to adapt to the AI.
Other providers also offer strong Arabic support. Konvergense advertises fluent Arabic capabilities in its voice assistants, and SAN Softwares lists Arabic as a supported language.
While global platforms like Yellow.ai offer Arabic support as part of their extensive language library, the depth of their dialectal understanding compared to the MENA-native specialists is a key point for evaluation.
The critical distinction is between a system that has been “taught” Arabic as a secondary language versus one that was “born” from Arabic data.
3.3 Enterprise Integration and Ecosystem
An AI voice agent’s effectiveness is significantly amplified by its ability to connect with and leverage data from other core business systems. This includes Customer Relationship Management (CRM), helpdesk, and e-commerce platforms.
This integration transforms the agent from an isolated answering machine into a fully-fledged component of the customer experience ecosystem.
Global platforms typically excel in this area due to their scale and established partner networks. Yellow.ai offers a marketplace of over 150 pre-built enterprise integrations.
This includes deep connections with major platforms like Salesforce, Zendesk, Genesys, Shopify, and Magento. This allows for rapid deployment and seamless data flow, enabling personalization based on a customer’s history and behavior.
The MENA specialists are also building robust ecosystems. Maqsam provides native integrations with widely used tools like Zendesk, Zoho, Intercom, Pipedrive, and Salesloft, covering key CRM and helpdesk functionalities.
They also offer integration with Freshdesk. For businesses with custom or in-house software, both Maqsam and Yellow.ai provide comprehensive API suites for custom integrations.
Local integrators like Konvergense and Nxtaa Technologies position their integration capabilities as a core part of their service. They promise to seamlessly connect their AI solutions with a client’s existing CRM, ERP, and communication platforms.
Providers like Awaz.ai leverage third-party integration platforms like Zapier and Make to connect with over 6,000 applications. This offers broad connectivity even without a large library of native integrations.
In contrast, some providers like Callab.ai state they offer CRM integration but do not publicly list their partners, requiring a direct sales engagement to assess their ecosystem.
3.4 Operational and Analytical Features
Beyond the core conversational capabilities, enterprise-grade voice agent solutions are differentiated by their operational robustness, security, and analytical tools.
Scalability is a primary concern for businesses in a high-growth market like Dubai. Providers need to demonstrate that their infrastructure can handle fluctuating call volumes without a degradation in service.
Konvergense, for example, explicitly claims its system can scale from 50 to 50,000 calls per day, while their infrastructure serves millions of monthly interactions.
Security and Compliance are non-negotiable, particularly in regulated industries like finance and healthcare. Nxtaa Technologies highlights its platform’s bank-grade security and compliance with international privacy standards.
Yellow.ai provides extensive compliance credentials, including HIPAA, SOC 2 Type II, and ISO 27001/27701. This offers a high degree of assurance for enterprises handling sensitive data.
Analytics and Reporting are essential for measuring ROI and driving continuous improvement. A strong platform provides more than just call logs. Nxtaa Technologies offers comprehensive conversation analytics, including sentiment analysis and performance metrics.
Callab.ai provides a centralized dashboard where every call is recorded, transcribed, and sentiment-tagged for review and action.
Maqsam offers real-time dashboards and custom reports designed for call center operations to track performance and analyze customer trends. These tools are critical for understanding agent performance, identifying common customer pain points, and optimizing conversational flows over time.
Part 4: Commercial and Implementation Models
Successfully deploying an AI voice agent requires a clear understanding of not only the technology but also the associated commercial structures and implementation methodologies.
For businesses in the UAE, this involves navigating a variety of pricing models to find the most cost-effective fit. It also means following a structured deployment lifecycle to ensure the project delivers on its strategic objectives.
A comprehensive evaluation must extend beyond the initial price tag to consider the total cost of ownership (TCO). This includes ongoing operational expenses, maintenance, and the internal resources required for a successful launch and continuous improvement.
4.1 Navigating Pricing Structures
The pricing models for AI voice agent solutions in the UAE vary significantly, reflecting the diversity of the providers themselves. Understanding these structures is key to aligning costs with expected usage patterns and business value.
Usage-Based Pricing: This model, often used by CPaaS providers and some specialized platforms, links costs directly to consumption. Plivo, an infrastructure provider, offers a clear example with its per-minute rates for calls within the UAE.
It charges approximately $0.2290/min for local outbound calls and $0.2660/min for mobile calls. This model is advantageous for businesses with highly variable or seasonal call volumes, as costs scale directly with usage. However, it can be difficult to budget for and may become expensive at very high volumes.
Subscription-Based Pricing (SaaS): This is a common model for platform providers and local integrators. Nxtaa Technologies, for instance, offers tiered subscription plans for its contact center solution.
Plans start from AED 199 per agent per month for a “Starter” plan to AED 399 per agent per month for a “Professional” plan, with custom pricing for enterprise needs. This model provides predictable monthly costs, making it easier to budget.
The value depends on maximizing the utilization of the features included in the subscription tier.
Project-Based/Fixed-Cost Pricing: This model is typical for custom development and consulting engagements. An analysis of the Dubai market suggests that the development cost for a custom AI chatbot or voice bot can range from AED 36,000 to AED 110,000, depending on complexity.
For more sophisticated, enterprise-grade AI platforms, costs can range from AED 700,000 to over AED 3 million. This model is suitable for well-defined projects with a clear scope, but it can be inflexible if requirements change.
Hybrid and Custom Models: Many providers offer flexible or custom pricing. Purple Rock emphasizes its “flexible, transparent pricing” model, which allows clients to modify their solutions and manage costs efficiently.
Other platforms, like Feedyou.ai, encourage potential clients to request a custom quote or use an online calculator to estimate savings, suggesting a value-based pricing approach.
A crucial consideration is the total cost of ownership, which extends far beyond these initial pricing structures. A typical AI project budget breakdown allocates only 25-35% to the core model development and training.
Significant additional costs include data preparation (20-30%), integration (15-20%), and, critically, ongoing deployment and maintenance (15-20%).
Furthermore, there are hidden operational costs to consider. These include cloud hosting and GPU resources (which can cost from $2 to $15 per hour for high-end instances), third-party API licensing fees, and the recurring cost of model retraining to prevent performance degradation over time.
A simplistic price comparison is therefore insufficient; a thorough financial evaluation must account for these ongoing operational and maintenance expenses to accurately project the long-term TCO.
4.2 The Path to Deployment: A Lifecycle Approach
Implementing an AI voice agent is not a one-time event but a strategic project that follows a distinct lifecycle. Synthesizing best practices from various providers and implementation guides reveals a structured, multi-phase approach that maximizes the chances of success.
Phase 1: Discovery & Strategy The foundation of any successful deployment is a clear definition of its purpose and scope. This initial phase involves deep collaboration between the business stakeholders and the technology team.
The primary goal is to identify specific, high-impact use cases. This can be achieved by analyzing current support operations to identify the most frequent and repetitive tasks that are suitable for automation.
It is crucial to set clear, measurable objectives from the outset, such as reducing average handling time, improving first-call resolution rates, or deflecting a certain percentage of inbound calls. Rushing this phase often leads to a solution that is technologically impressive but fails to solve a real business problem.
Phase 2: Design & Data Preparation Once the strategy is defined, the focus shifts to designing the user experience. This involves mapping out common customer scenarios and designing intuitive, natural-feeling conversational flows that mimic human dialogue.
A key activity in this phase is dialog flow design, which outlines the potential paths a conversation can take. Simultaneously, the knowledge base that will power the agent must be developed.
This involves compiling and structuring the data the agent will need to answer questions accurately. This data could come from FAQs, product manuals, or internal databases. Data quality is paramount, as the agent’s performance will be a direct reflection of the data it is trained on.
Phase 3: Build & Train In this phase, the agent is constructed. This may involve using a no-code, drag-and-drop platform, as offered by providers like Awaz.ai, which significantly accelerates development time.
Alternatively, it could involve custom coding for more complex, bespoke requirements. Following the initial build, the agent must be rigorously trained.
This involves feeding the AI model with large datasets of relevant conversations and queries. This teaches it to recognize user intent and provide accurate responses. This training should include variations of common requests and industry-specific terminology to ensure the agent can handle real-world interactions.
Phase 4: Integration & Testing An AI agent’s value is maximized when it operates as part of a connected ecosystem. This phase focuses on integrating the voice agent with existing business systems, most importantly the CRM.
This allows the agent to access customer history for personalized interactions and to log new interactions for a unified customer view. Following integration, extensive testing is critical.
This should go beyond simple functional tests to include user acceptance testing (UAT). Real users should evaluate the naturalness of the conversation, the accuracy of the responses, and the effectiveness of the escalation paths to human agents.
Phase 5: Launch & Optimization The final phase involves deploying the AI agent into the live environment. However, the work does not end at launch. The most successful deployments treat the voice agent as a dynamic system that requires continuous improvement.
This involves establishing monitoring dashboards to track key performance indicators (KPIs) like call resolution rates and customer satisfaction scores.
Transcripts of conversations should be reviewed regularly. This helps identify areas where the agent struggled or where the conversational flow can be improved. This data-driven feedback loop allows for ongoing refinement and retraining of the AI model, ensuring that the agent becomes more intelligent and effective over time.
Part 5: Strategic Recommendations for Selection and Deployment
The successful adoption of an AI voice agent in the competitive Dubai market is contingent on two critical factors: selecting the right provider and executing a well-planned implementation strategy.
The preceding analysis provides the foundational knowledge to inform these decisions. This final section synthesizes these findings into an actionable decision-making framework and a practical checklist.
This is designed to guide enterprises from strategic consideration to successful, value-driven deployment. The ultimate goal is to move beyond a simple technology purchase towards the integration of a strategic asset that enhances customer experience, improves operational efficiency, and unlocks new avenues for growth.
5.1 The Provider Selection Matrix: A Decision-Making Framework
The diverse provider landscape requires a strategic approach to selection. This means moving beyond a feature-for-feature comparison to an assessment of which provider best aligns with the organization’s core priorities and operational model.
Answering the following key strategic questions will help narrow the field and identify the most suitable partner:
What is the primary linguistic priority? If flawless, dialect-aware Arabic communication is a non-negotiable, mission-critical requirement, the selection process should heavily favor the Specialized MENA-Focused Platforms.
Providers like Maqsam and Callab.ai, who have built their technology from the ground up with a deep understanding of regional dialects and cultural nuances, offer a distinct advantage that global platforms may struggle to match. Their “Arabic-first” approach is designed to handle the complexities that are most relevant to the local customer base.
What is the long-term platform strategy? If the objective is to implement a single, unified, global platform to manage all customer interactions (voice, chat, email, social) in a consistent manner, then a Global Omnichannel Conversational AI Platform like Yellow.ai is the logical choice.
Their strength lies in providing a comprehensive, scalable, and feature-rich solution with a vast ecosystem of integrations. This makes them ideal for large enterprises seeking standardization across multiple geographies and channels.
What is the availability of internal resources? If the organization lacks a dedicated internal team with the expertise to manage a complex AI project and its integration into the existing tech stack, partnering with a Local/Regional IT Integrator is the most prudent path.
Companies like Konvergense and Nxtaa Technologies offer a full-service partnership model. They bring not only the technical skills to build and deploy the voice agent but also the local market knowledge and project management capabilities to guide the entire process, acting as an extension of the client’s team.
What is the degree of required customization? If the intended use case is highly specific to the business, involving proprietary processes or unique conversational flows that cannot be accommodated by an existing platform, then a Custom Development & Consulting Agency is the appropriate choice.
This “Build” approach, offered by firms like Cezcon Solutions or Infomates Technologies, provides maximum flexibility to create a truly bespoke solution, albeit with potentially higher upfront costs and longer development timelines.
5.2 A Checklist for Successful Implementation in Dubai
A successful deployment is as much about process as it is about technology. The following checklist synthesizes best practices tailored for the specific context of the Dubai market:
Secure Executive Stakeholder Alignment: Begin by building a robust business case that resonates with senior leadership. Utilize UAE-specific data, such as the finding that 77% of local firms see significant productivity gains from AI.
Show that over 44% expect ROI within a year to demonstrate a clear path to value. Frame the investment not as a cost center but as a strategic enabler of growth and innovation.
Establish Robust Data Governance: From the outset, ensure that all data collection, processing, and storage practices are compliant with UAE regulations. Given the increasing focus on data privacy, building a solution with compliance at its core is essential for long-term viability and risk mitigation.
Prioritize an Authentic Arabic User Experience (UX): Do not treat Arabic support as a simple translation exercise. Involve native Arabic speakers, ideally those familiar with local dialects, in the design and testing of conversational flows.
This ensures the agent’s language is not only accurate but also culturally appropriate and natural-sounding. This is critical for user adoption and trust.
Launch with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP): Resist the temptation to build an all-encompassing solution from day one. Start with a narrow, well-defined scope, such as automating the top 3-5 most frequently asked questions or a single transactional process like appointment booking.
This allows for a faster launch, provides an opportunity to gather real-world data, and demonstrates value quickly, building momentum for future expansion.
Integrate, Don’t Isolate: Plan for deep integration with your CRM and other systems of record from the very beginning of the project. An integrated agent can provide highly personalized and context-aware interactions, dramatically improving the customer experience and the operational value of the solution.
Position as Augmentation, Not Replacement: Communicate the AI agent’s role internally as a tool to augment and support human agents, not replace them.
By automating repetitive, low-value tasks, the voice agent frees up human employees to focus on more complex, empathetic, and strategic customer interactions. This approach not only improves efficiency but also enhances employee satisfaction and reduces burnout.
Commit to a Cycle of Measurement and Iteration: Establish clear KPIs before launch, such as call deflection rate, customer satisfaction (CSAT) scores, average handling time, and resolution rates.
Use the analytics provided by the platform to continuously monitor performance against these KPIs. Create a feedback loop for ongoing optimization. The best AI voice agents are not built; they evolve.
5.3 Future Outlook: The Rise of Agentic AI in the Middle East
The current landscape of AI voice agents, while impressive, represents only the beginning of a profound technological shift. The future of conversational AI in the Middle East is moving rapidly towards more autonomous, proactive systems often described as “agentic AI.”
This next wave of technology will see AI systems capable of not just responding to queries but of executing complex, multi-step tasks and making decisions to achieve a specified goal.
Providers in the market are already embracing this evolution. Yellow.ai, for example, is explicitly positioning its offering as an “Enterprise-grade Agentic AI Platform.” This signals a move beyond simple conversation automation to full business process automation.
This evolution is supported by massive strategic investments in AI by regional governments. National transformation programs like the UAE’s AI Strategy 2031 and Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 are channeling billions of dollars into AI development, creating an environment ripe for rapid innovation.
For businesses in Dubai, this means that the strategic value of conversational AI will only increase. Today’s voice agent that books an appointment may, in the near future, be an AI agent that manages the entire patient intake process.
This could range from scheduling and insurance verification to pre-visit instructions and post-visit follow-up. The AI agent that qualifies a real estate lead today may soon be one that can conduct virtual property tours, process initial paperwork, and coordinate with multiple stakeholders.
As the technology matures from conversational tools to autonomous agents, it will become an even more integral driver of operational efficiency, customer loyalty, and strategic differentiation in the dynamic and forward-looking economy of the UAE.

