Intelligent interaction and communication with customers using Artificial Intelligence
The landscape of customer interaction is undergoing a seismic shift, moving beyond rudimentary automation to a new era of intelligent, adaptive, and proactive engagement.
This evolution is driven by the strategic application of Artificial Intelligence (AI), which is fundamentally reshaping how businesses communicate with their customers. The emerging paradigm, known as Intelligent Customer Experience (ICX), represents a departure from legacy systems, creating a strategic capability that drives loyalty, efficiency, and growth.
Defining Intelligent Interaction: From Automation to Augmentation
At its core, AI in customer service is the application of advanced technologies to streamline support, personalize interactions, and assist customers with unprecedented speed and efficiency, often minimizing the need for direct human involvement. However, this definition only scratches the surface of a more profound transformation.

The modern approach is best encapsulated by the concept of Intelligent Customer Experience (ICX), which leverages a synthesis of AI, automation, and data analytics to deliver experiences that are not just reactive but proactively personalized.
ICX is a revolutionary advancement from traditional Customer Experience (CX). While conventional CX strategies focus on optimizing existing touchpoints, ICX harnesses emerging technologies like generative AI and advanced automation to fundamentally reinvent those touchpoints.
The critical distinction lies in the transition from static, rule-based automation—systems that follow a predefined script—to dynamic, cognitive systems.

These intelligent systems learn from every interaction, predict customer needs, and adapt their responses in real time, moving from simple task execution to genuine problem-solving and experience enhancement.
The Technology Stack: Deconstructing the AI Engine
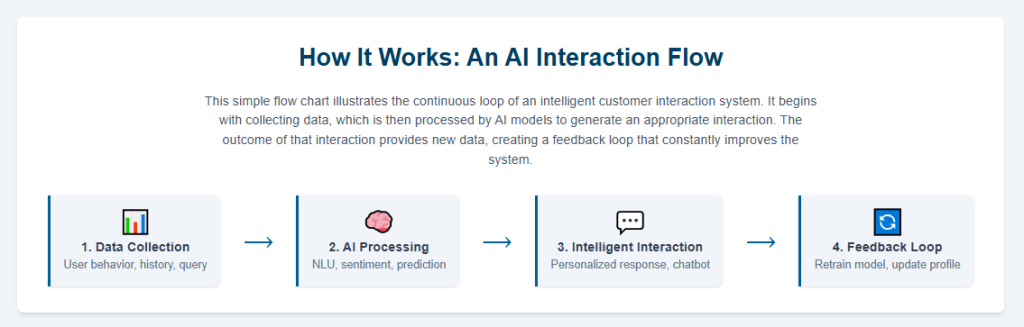
The power of ICX is not derived from a single technology but from the synergistic integration of several core components that collectively create a system designed to understand, learn, and respond in a manner that mimics human interaction. This technological synthesis is what imbues the experience with “intelligence.”
Natural Language Processing (NLP): This is the foundational layer, enabling machines to comprehend, interpret, and generate human language.
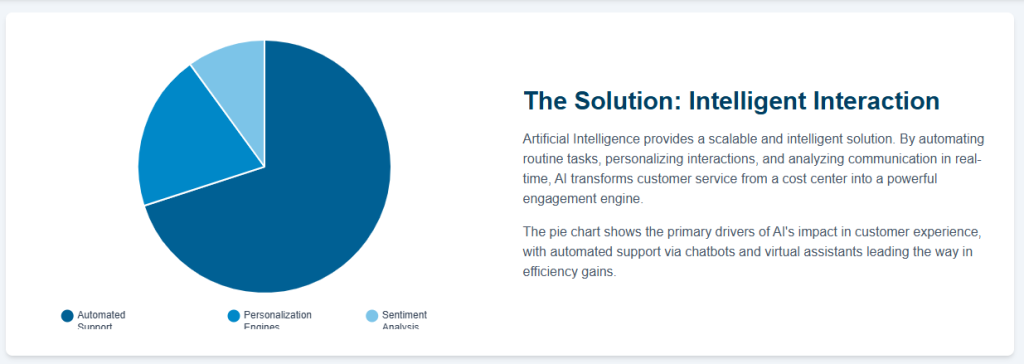
NLP allows AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants to understand the intent behind a customer’s query, regardless of how it is phrased, thereby reducing misunderstandings and improving the quality of engagement.
Machine Learning (ML): ML serves as the engine of continuous improvement. By analyzing vast datasets of past customer interactions, ML algorithms identify patterns, predict future needs, and refine the system’s performance over time without requiring manual updates.
This learning capability ensures that the AI becomes progressively more accurate and effective with each conversation.
Generative AI: A transformative and more recent addition, generative AI elevates interactions beyond pre-scripted answers. It can create novel, dynamic, and context-aware content on the fly.
This includes drafting personalized email responses, summarizing long conversation histories for human agents, and even generating new articles for a company’s knowledge base, making interactions more fluid and comprehensive.
Sentiment Analysis: This technology functions as AI’s emotional barometer. By analyzing the language, tone, and even speech patterns in a customer’s message, sentiment analysis can detect emotions such as frustration, anger, or happiness.
This allows the system to prioritize urgent issues, route distressed customers to human agents, and enable more empathetic and appropriate responses.
Predictive Analytics: This forward-looking component analyzes historical data and real-time behavioral patterns to anticipate future customer needs.
It can identify a customer at risk of churning, predict that a service is about to lapse and send a proactive reminder, or forecast seasonal demand for support services, enabling businesses to address issues before they escalate.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Often working in tandem with more cognitive AI technologies, RPA handles repetitive, rule-based back-office tasks such as data entry or system updates.
By automating these processes, RPA frees human agents to concentrate on higher-value activities that require emotional intelligence and creative problem-solving.
The Business Imperative: From Cost Center to Strategic Differentiator
The integration of AI into customer communication is no longer merely an operational tactic for cost reduction; it has become a strategic imperative for competitive differentiation.
In today’s market, customer experience has emerged as a primary determinant of brand loyalty, and AI provides a decisive edge by enabling businesses to analyze customer behavior in real time, anticipate needs, and resolve issues proactively.
The modern business mandate is to leverage this technological stack to consistently exceed evolving customer expectations at scale.
This technological shift fundamentally alters the financial and strategic role of the customer service department. Traditionally viewed as a cost center to be minimized, the function is now being reframed as a powerful revenue generator.
When an AI agent can analyze a customer’s purchase history during a support interaction and proactively recommend a relevant product or service, it transforms a support ticket into a sales opportunity. This capability changes the entire calculus of investment.
The return on investment (ROI) for AI in customer communication is no longer measured solely by “costs saved” through automation but by the more compelling metric of “costs saved plus net new revenue generated.”
This reframes the investment from a necessary operational expense into a strategic growth initiative, making a far stronger case for executive buy-in and resource allocation.
AI in Action: Applications Across the Customer Journey
The technologies underpinning Intelligent Customer Experience are being deployed across the entire customer lifecycle, breaking down traditional departmental silos and creating a unified, data-driven approach to engagement.
From initial service inquiries to personalized marketing campaigns and streamlined sales processes, AI is revolutionizing how businesses interact with their customers at every touchpoint.
Revolutionizing Customer Service
24/7 Self-Service (Chatbots & Virtual Assistants): The most visible application of AI in customer service is the deployment of chatbots and virtual assistants that provide instant, around-the-clock support.
A crucial distinction exists between rudimentary rule-based bots, which follow a strict script, and advanced AI-powered Virtual Customer Assistants (VCAs).
VCAs leverage NLP and ML to handle more complex, multi-step tasks such as placing orders, troubleshooting technical problems, or resolving account-specific issues, offering a far more sophisticated self-service experience.
Intelligent Routing and Triage: AI systems can automatically analyze incoming support tickets, emails, and messages. Using NLP to understand the topic and sentiment analysis to gauge urgency, the system intelligently routes the inquiry to the most qualified agent or department.
This eliminates manual sorting, reduces wait times, and significantly boosts agent efficiency and first-contact resolution rates.
Agent-Assist and Augmentation: Rather than replacing human agents, AI is increasingly serving as their “copilot.” Agent-assist tools work within the agent’s interface to provide real-time support.
They can instantly summarize long conversation histories, surface relevant articles from the knowledge base, provide customer data from the CRM, and even suggest the next best action or response.
This augmentation empowers agents to resolve issues faster and more accurately, reducing average handle time and improving the overall quality of service.
Proactive and Predictive Support: A paradigm-shifting application is the move from reactive to predictive support. By analyzing data patterns, AI can identify potential issues before a customer is even aware of them.
For example, it might detect unusual account activity and flag it for security, notice a subscription is about to lapse and send a renewal offer, or identify a customer who is struggling with a product feature and proactively provide a tutorial.
This preventative approach dramatically enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Transforming Marketing and Personalization
Hyper-Personalization at Scale: This is the cornerstone of AI’s application in marketing. AI algorithms can analyze immense volumes of customer data—including browsing history, past purchases, demographic information, and real-time behavior—to tailor every message, product recommendation, and offer to the individual user.
This allows businesses to move beyond generic campaigns and deliver millions of unique, one-to-one experiences simultaneously.
Predictive Analytics for Customer Behavior: AI models can forecast future customer actions with a high degree of accuracy. This includes predicting a customer’s lifetime value (CLTV), identifying individuals at high risk of churning, and even forecasting the date of their next purchase.
These insights allow marketers to deploy proactive retention campaigns, focus resources on high-value customer segments, and optimize their strategies for long-term growth.
Dynamic Content and Campaign Optimization: AI is automating the creative and optimization processes. Generative AI can create on-brand email subject lines, SMS copy, and personalized product descriptions.
Furthermore, AI systems can conduct continuous A/B testing on various campaign elements—such as send times, channels, and creative content—and automatically allocate resources to the winning variations, ensuring ongoing performance improvement without manual intervention.
AI-Assisted Segmentation: The process of creating target audiences is also being streamlined. Marketers can now use natural language to describe the segment they wish to target (e.g., “high-value customers who have not purchased in 90 days but have recently browsed our new product line”).
The AI will then analyze all available behavioral and predictive data to build and populate this highly specific segment in seconds.
Empowering Sales and Lead Generation
Predictive Lead Scoring and Qualification: AI algorithms analyze data from incoming leads and compare it against historical data of successful conversions. By identifying key characteristics and behaviors, the system can assign a “lead score” that predicts the likelihood of conversion.
This allows sales teams to stop chasing unqualified leads and focus their time and energy on the prospects with the highest potential.
Automated and Personalized Outreach: AI agents are capable of managing complex prospecting workflows. They can conduct initial account research, identify key decision-makers within an organization, and then craft and deploy hyper-personalized outreach sequences across multiple channels like email and social media.
This automates the time-consuming top-of-funnel activities, allowing salespeople to engage when a lead is already warmed up.
Sales Process Automation: AI significantly reduces the administrative burden on sales professionals. It can automate CRM data entry, generate more accurate sales forecasts by analyzing historical data and predictive insights, and automatically transcribe and summarize sales calls.
This automation frees up a significant amount of time, enabling sellers to focus on what they do best: building relationships and closing deals.
Data-Driven Sales Insights: By analyzing every interaction—from email responses to call transcripts—AI can provide actionable insights to refine sales strategies.
It can identify which messaging resonates most with certain personas, determine the most effective ways to handle common objections, and flag deals that are at risk based on engagement patterns. This data-driven coaching helps improve the performance of the entire sales team.
The deployment of AI across these functions reveals a powerful underlying trend: AI is not merely optimizing individual departments in isolation but is acting as a unifying data and intelligence layer that breaks down traditional organizational silos.
A customer service complaint analyzed by AI for sentiment can trigger a marketing workflow to pause a promotional campaign for that user, while simultaneously alerting the sales team to a potential relationship risk.
This interconnectedness means that a successful AI strategy is inherently cross-functional, demanding a unified customer data platform and close collaboration between service, marketing, and sales leadership.
Furthermore, a clear pattern emerges in how AI impacts the human workforce. In every function, AI automates the repetitive, data-heavy, and administrative tasks—answering FAQs, running A/B tests, qualifying leads.
This systematically shifts human labor up the value chain. The role of the human professional is evolving to focus on tasks that require uniquely human skills: high-level strategy, creative problem-solving, complex negotiation, and genuine emotional intelligence.
This has profound implications for organizational design, necessitating a strategic focus on retraining and upskilling the workforce to prepare for a future where their primary role is to complement, rather than compete with, their AI counterparts.
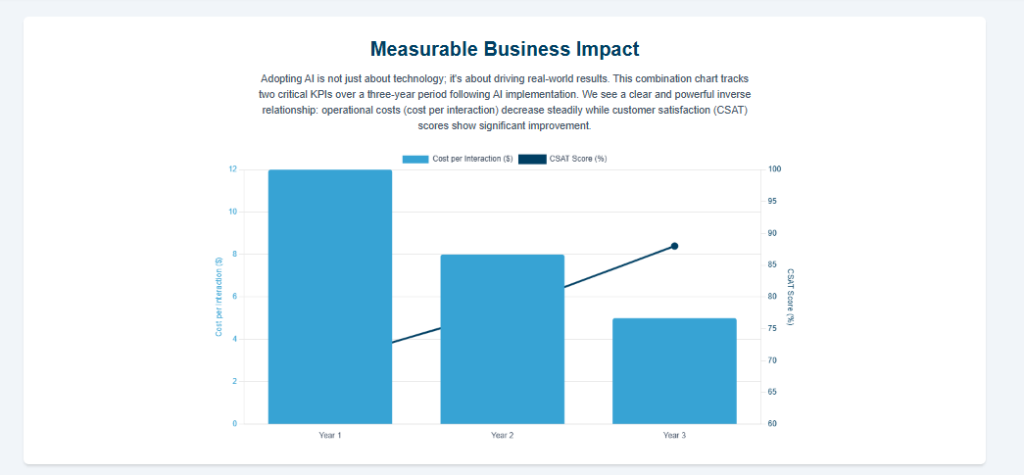
Strategic Value and Proven Impact: A Data-Driven Analysis
The theoretical benefits of AI in customer communication are substantiated by a growing body of evidence from real-world implementations. Organizations across industries are realizing tangible returns on their AI investments, measured through improved efficiency, enhanced customer satisfaction, and increased productivity.
A data-driven analysis of these outcomes, supported by specific case studies, demonstrates the profound and quantifiable impact of intelligent communication strategies.
Quantifiable Business Benefits: The ROI of Intelligent Communication
Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction: One of the most immediate benefits of AI is its ability to drive down operational costs. By automating routine inquiries and processes, AI can handle thousands of customer interactions simultaneously, 24/7, without the associated labor costs.
Research from Juniper projects that chatbots alone will be responsible for over $8 billion in annual cost savings for businesses. This is exemplified by the digital insurance agency Nsure.com, which leveraged Azure OpenAI Service to automate processes and successfully lowered its operational costs by 50%.
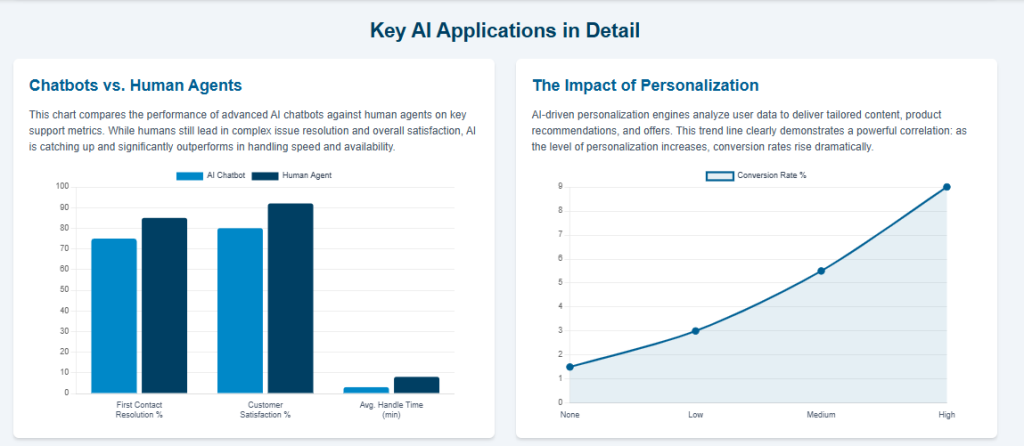
Enhanced Agent Productivity: AI empowers human agents to accomplish more with less effort. By deflecting simple, repetitive questions, AI frees up agents to focus on more complex, high-value interactions.
Mature adopters of AI have reported a 38% lower average call handling time for their human agents. A global camping company that implemented an IBM cognitive tool in its contact center saw a 33% increase in overall agent efficiency.
Furthermore, early pilots of generative AI have shown the potential to reduce the average handling time for agents by as much as 30%.
Improved Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) and Loyalty: The speed, availability, and personalization enabled by AI directly translate to a better customer experience. With 71% of modern consumers expecting personalized interactions, AI’s ability to tailor responses and recommendations is critical.
The primary drivers of customer frustration—long wait times and friction in the support process—are significantly mitigated by AI’s instant response capabilities. This leads to higher satisfaction, which in turn fosters loyalty and reduces churn.
Scalability and 24/7 Availability: AI-driven support tools operate around the clock, ensuring that customers can get assistance at any time, which 51% of consumers now expect as a standard.
This constant availability allows businesses to handle massive and fluctuating volumes of customer requests without the need to proportionally increase their support staff, providing a scalable solution for growth.
Case Study Deep Dive: AI Implementation in the Real World
Examining specific implementations reveals how leading organizations are translating AI capabilities into strategic success. These cases are not merely technological showcases; they are examples of business-led strategies that solve specific, measurable problems.
Amtrak (“Julie”): The U.S. passenger railroad service deployed “Julie,” an AI-powered virtual assistant, to manage high-volume customer inquiries. In a single year, Julie handled over 5 million requests, resulting in a 25% increase in self-service bookings and a significant reduction in the workload for human agents.
The strategic lesson here is the successful application of AI in a high-volume, transactional environment to drive a specific business outcome: increased direct bookings.
Bank of America (“Erica”): This virtual financial assistant demonstrates AI’s utility in a sensitive and complex domain. Erica handles over 2 million customer requests daily, resolving 78% of them in an average of just 41 seconds.
Key to its success has been a commitment to continuous improvement, with over 60,000 updates made to its conversational AI. This case illustrates how trust and utility can be built through relentless iteration and a focus on conversational design, even in a highly regulated industry.
Verizon (Predictive Support): Verizon provides a powerful example of shifting from a reactive to a proactive support model. The company uses generative AI to predict the reason behind 80% of its 170 million annual customer calls.
This foresight allows for more effective routing and proactive solutions, which has enabled Verizon to prevent an estimated 100,000 potential churn cases each year. This highlights the immense financial impact of using predictive analytics to directly address customer retention.
Lyft (Agent Assist): Demonstrating the power of AI as an internal empowerment tool, Lyft integrated Anthropic’s Claude AI into its support systems. The result was a staggering 87% reduction in the average resolution time for its human support agents.
This case study proves that some of the most significant gains from AI can be realized by augmenting the human workforce, leading to massive improvements in internal efficiency.
Spotify & Netflix (Personalization Engines): These digital giants exemplify how AI-driven personalization can become the core of a business model. Spotify’s “Discover Weekly” playlists and Netflix’s recommendation engine—which accounts for an estimated 80% of all content watched on the platform—show how AI can drive user engagement, satisfaction, and retention on a massive scale.
Their success teaches that for some businesses, AI personalization is not just a feature but the fundamental value proposition.
A common thread connects these successful implementations: they were not technology-led projects but business-led initiatives. Amtrak aimed to increase bookings, Verizon to reduce churn, and Lyft to decrease resolution time.
They each identified a clear, quantifiable business problem and then applied AI as the solution. This goal-oriented approach is far more likely to deliver a demonstrable ROI than a vague mandate to “implement AI.”
Furthermore, the scale of data is a critical determinant of AI’s impact. Companies like Bank of America and Verizon process millions of interactions, providing a rich stream of data that fuels their machine learning models.
The more data an AI system processes, the more it learns, and the more accurate and effective it becomes. This implies that the business case for highly sophisticated, self-learning AI is strongest in high-volume environments.
For smaller organizations, the strategy may focus less on training models on their own limited data and more on leveraging pre-trained models or simpler, more accessible AI tools.
The Human-AI Symbiosis: Navigating the New Support Landscape
The rise of AI in customer communication does not signal the end of human involvement. Instead, it heralds a new era of human-AI collaboration.
The optimal strategy is not one of replacement but of intelligent integration, creating a symbiotic relationship where technology handles scale and efficiency, while humans provide empathy and complex problem-solving. This hybrid model is emerging as the imperative for navigating the new support landscape.
AI vs. Human Agents: A Comparative Analysis
Understanding the distinct strengths and weaknesses of both AI and human agents is crucial for designing an effective hybrid strategy.
AI Strengths: The primary advantages of AI are rooted in its computational nature. It offers unparalleled speed, providing instantaneous responses; 24/7 availability, operating without breaks; immense scalability, handling thousands of conversations simultaneously; and perfect consistency in its responses.
It excels at data-driven, repetitive tasks where accuracy and efficiency are paramount.
Human Strengths: Human agents excel where AI currently falls short. Their core strengths are empathy and emotional intelligence, allowing them to understand and respond to a customer’s emotional state.
They possess superior creative problem-solving abilities, enabling them to navigate complex, ambiguous, or novel issues that do not fit a predefined pattern. Most importantly, humans can build genuine relationships and trust through personal connection, a critical component of long-term customer loyalty.
Customer Preferences: Customer preference often depends on the nature of the inquiry. While many customers appreciate the speed of AI for simple issues, a significant portion—52% according to one survey—still prefer human interaction, particularly for the empathy it provides in complex or sensitive situations.
However, a growing number (42%) value a hybrid approach that combines the best of both. Ultimately, customers do not inherently dislike AI; they dislike inefficient AI that wastes their time. The quality of the interaction, and especially the transition between AI and human, is what truly matters.
The Hybrid Model Imperative: Architecting a Seamless Experience
A hybrid model is a strategic framework that combines AI-powered automation for routine, high-volume tasks with skilled human agents for complex, emotionally charged, or high-value interactions.
The objective is to create a seamless customer journey that leverages AI’s efficiency without sacrificing the critical human touch.
Best Practices for Implementation:
Use AI as the First Layer: AI should serve as the initial point of contact to handle common questions, categorize issues, and gather preliminary information. This acts as an intelligent filter, deflecting a significant volume of low-complexity tickets and allowing human agents to focus where they are needed most.
Ensure a Seamless Handoff: The transition from an AI bot to a human agent is the most critical and failure-prone moment in a hybrid interaction. A successful handoff must be fluid, with the full context of the AI conversation—including customer information and steps already taken—passed seamlessly to the human agent.
This prevents the cardinal sin of customer service: forcing the customer to repeat themselves. Investing in the “connective tissue” that integrates AI and human workflows is as important as investing in the AI technology itself.
Empower, Don’t Replace: The most effective hybrid models use AI to augment human capabilities. By providing agents with real-time data, customer history, and AI-generated response suggestions, businesses can transform their support staff into “super-agents” who are better informed and more efficient.
Maintain Clear Escalation Paths: A customer should never feel trapped in a conversation with a bot. There must always be a clear, simple, and readily available option to escalate the interaction to a human representative. This provides a crucial safety net and builds customer trust in the automated system.
The strategic decision of where to deploy AI versus human agents can be guided by a clear comparison of their core attributes.
Comparative Analysis of AI-Driven vs. Human-Led Communication
| Attribute | AI-Driven Communication | Human-Led Communication | Strategic Implication for Hybrid Model |
| Availability | 24/7/365 | Limited by Business Hours & Shifts | Use AI for after-hours and overflow support to ensure constant availability. |
| Scalability | Near-infinite; handles thousands of concurrent interactions | Limited by headcount and training | Deploy AI to manage high-volume, predictable inquiries, reserving human agents for manageable queues. |
| Cost per Interaction | Extremely low | High (salaries, benefits, training) | Automate low-value, high-frequency tasks with AI to optimize cost-efficiency. |
| Speed (First Response) | Instantaneous | Subject to queues and wait times | Leverage AI for all initial contacts to eliminate wait times and improve first-response metrics. |
| Consistency | Perfectly uniform and compliant with scripts | Variable by agent skill, mood, and training | Use AI for tasks requiring strict compliance and consistency, such as policy explanations. |
| Emotional Intelligence | Low (simulated via sentiment analysis) | High (genuine empathy and understanding) | Escalate emotionally charged or sensitive conversations immediately to human agents. |
| Complex Problem-Solving | Limited (pattern-based, struggles with novelty) | High (creative, contextual, and adaptive) | Route all non-standard, multi-faceted, or ambiguous issues to human experts. |
| Building Trust & Rapport | Low; transactional in nature | High; capable of building long-term relationships | Reserve human agents for high-value customers or critical moments that define the customer relationship. |
This comparative analysis makes the case for a hybrid model self-evident. A business leader must constantly balance the competing pressures of cost, quality, and scale.
The table visually demonstrates how AI can solve for cost and scale on routine issues, which in turn liberates the more expensive and finite human resources to deliver superior quality and empathy on the complex issues that truly define the customer experience. This strategic allocation of resources optimizes the entire support ecosystem.
This shift also redefines the role of the human agent. As AI handles an increasing number of transactional inquiries, the problems that escalate to humans are, by nature, more complex, emotionally charged, and relationship-critical.
Consequently, the role of the frontline agent is evolving from a transactional “problem solver” to a high-value “relationship builder.”
The most valuable skills for this new role are not speed or script adherence, but high emotional intelligence, critical thinking, and the ability to act as a true brand ambassador. This evolution has profound implications for how organizations hire, train, and measure the performance of their customer-facing teams.
Navigating the Risks: Ethical Considerations and Governance
The rapid integration of AI into customer interactions, while offering immense benefits, also introduces significant ethical challenges and risks.
A responsible implementation requires a robust governance framework that addresses data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential for depersonalized experiences. Navigating these complexities is not merely a matter of compliance; it is a strategic necessity for building and maintaining customer trust.
The Privacy Paradox: Personalization vs. Protection
A central tension exists in the age of AI: customers increasingly demand the hyper-personalized experiences that AI can deliver, yet they are simultaneously deeply concerned about the privacy of the data required to create those experiences.
Research indicates that 85% of consumers believe it is important for businesses to consider ethics when using AI technology. A failure to manage this paradox can quickly erode customer trust.
A strong governance framework is essential. This includes:
Obtaining Explicit Consent: Businesses must be transparent with customers about what data is being collected and how it will be used, obtaining their explicit consent before processing it.
Ensuring Data Security: Implementing robust security measures, such as end-to-end encryption, strict access controls, and regular security audits, is critical to protect sensitive customer data from breaches and comply with regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Maintaining Transparency: Companies should clearly communicate their AI and data usage policies, giving users control over their information and the ability to opt out of AI-driven interactions.
Algorithmic Bias and Fairness
AI systems are not inherently objective; they are a reflection of the data on which they are trained. If the training data contains pre-existing societal biases, the AI model can learn, perpetuate, and even amplify these biases, leading to discriminatory outcomes in areas like loan approvals, product recommendations, or service prioritization.
Mitigating this risk requires a proactive approach:
Regular Audits: AI systems must be continuously audited and monitored to detect and correct for biased patterns in their decision-making processes. This includes conducting third-party audits to ensure impartiality.
Diverse and Representative Training Data: A concerted effort must be made to train AI models on datasets that are diverse and inclusive, accurately reflecting the customer base and preventing the system from favoring certain groups over others.
Transparency and Explainability: One of the greatest challenges is the “black box” problem, where the internal logic of a complex AI model is opaque and unintelligible.
If a customer is adversely affected by an AI decision and the company cannot explain why that decision was made, trust is immediately destroyed. Businesses should strive to use AI models that offer some degree of interpretability and be prepared to provide clear explanations for their systems’ actions, which is crucial for accountability.
The Challenge of Depersonalization and Lack of Empathy
A significant ethical risk of over-relying on automation is the creation of sterile, depersonalized customer experiences. While efficient, AI can lack the genuine empathy and nuanced understanding required in sensitive or emotionally charged situations.
A single bad interaction with an unhelpful or unempathetic system can ruin a customer’s day and drive them to a competitor.
Maintaining the human element is paramount:
Human Oversight: It is critical to maintain human oversight of AI systems, empowering agents to intervene when an AI is struggling or when a situation requires empathy that a machine cannot provide. AI should be treated as a sidekick to human agents, not a wholesale replacement.
Transparency with Customers: Businesses should always be transparent when a customer is interacting with an AI bot. This manages expectations and gives the customer the agency to request a human if they prefer, which builds trust.
Clear Accountability: Organizations must establish clear lines of accountability for the actions and outcomes of their AI systems. A business cannot deflect responsibility by blaming the algorithm; it must own the results of the technology it deploys.
Ultimately, approaching AI ethics is not a defensive compliance exercise but a proactive strategy for building a source of competitive advantage.
In an environment where consumers are increasingly aware of and concerned about these issues, a demonstrable commitment to ethical AI can differentiate a brand, build a stronger reputation, and foster the deep-seated trust that underpins long-term customer loyalty.
The Market Landscape and Platform Ecosystem
The rapid expansion of AI in customer communication has given rise to a dynamic and diverse market of technology providers. Understanding this ecosystem is crucial for any organization looking to develop and implement an intelligent interaction strategy.
The landscape is broadly composed of integrated platform providers, specialized tool developers, and the foundational technology giants that power the entire industry.
Leading Platform Providers
The market for AI-powered customer communication tools is fragmenting, offering businesses a strategic choice between comprehensive, all-in-one solutions and best-in-class specialized applications.
Integrated Suite Platforms: Companies like Zendesk and Freshdesk offer comprehensive customer service platforms that bundle a wide range of functionalities—including ticketing systems, knowledge base management, and analytics—with increasingly sophisticated AI features.
Their value proposition is a unified, integrated solution that serves as a single source of truth for all customer interactions, simplifying data management and workflows.
Conversational AI Specialists: Providers such as LivePerson, Ada, and Intercom focus intensely on delivering advanced conversational AI. Their platforms are built around powerful, often generative AI-driven chatbots and messaging capabilities designed for deep, personalized engagement across multiple digital channels.
These specialists aim to provide the most sophisticated and human-like automated conversations available.
Sales and Marketing Focused Platforms: A distinct category of providers, including Drift and Klaviyo, leverages AI primarily to drive commercial outcomes. Their tools are optimized for lead generation, automated prospect qualification, and the delivery of hyper-personalized marketing campaigns.
The focus is on using conversational AI to move customers through the sales and marketing funnel.
Emerging No-Code Platforms: A new wave of companies, such as Wonderchat, is democratizing access to this technology. They offer no-code platforms that allow businesses, even those without dedicated development teams, to create, train, and deploy custom AI chatbots quickly and easily.
This trend is lowering the barrier to entry for smaller organizations to adopt AI-powered communication.
This fragmentation presents a critical strategic decision for business leaders. Adopting a single, integrated suite from a provider like Zendesk offers simplicity, data cohesion, and potentially lower total cost of ownership.
Conversely, pursuing a “best-of-breed” approach by integrating multiple specialized tools—for example, combining Ada’s chatbot with a separate CRM and marketing platform—may offer superior performance in each specific function but at the cost of increased complexity, integration challenges, and higher management overhead.
The right choice depends on an organization’s size, technical maturity, and strategic priorities.
Foundational Technology Enablers
Underpinning the entire ecosystem of specialized applications are the foundational technology giants. Companies like Google (DeepMind), Microsoft (Azure AI, OpenAI), Amazon Web Services (AWS), and IBM (Watson) develop the core large language models (LLMs) and provide the scalable cloud infrastructure that most other platforms are built upon.
Their continuous innovation in fundamental AI research is the engine that fuels the advancements seen across the entire market, from the most sophisticated enterprise solutions to the simplest no-code chatbot builders.
The Horizon: Future Trends in Intelligent Communication
The current state of AI in customer communication, while transformative, is merely a prelude to a more profound evolution.
The next wave of innovation will push beyond responsive systems to create proactive, autonomous, and emotionally aware ecosystems that will once again redefine the boundaries of customer interaction.
The Rise of Agentic AI: From Answering to Acting
The future lies in the transition from AI that answers questions to AI that acts to solve problems. This is the domain of agentic AI—autonomous systems that can interpret high-level goals and independently execute the complex, multi-step tasks required to achieve them with minimal human intervention.
Unlike a traditional chatbot that can only provide information, an agentic AI could, for example, handle an entire billing dispute autonomously.
It would access the customer’s account, analyze transaction history to identify the discrepancy, apply the necessary correction or credit, update the billing system, and then notify the customer of the resolution, all without human input. This represents a monumental leap from conversation to autonomous action.
Emotionally Intelligent AI: The Empathy Engine
The next frontier in making AI interactions feel truly human is the development of more sophisticated emotional intelligence, also known as affective computing.
Future AI systems will become far more adept at recognizing, interpreting, and responding appropriately to a wide spectrum of human emotions.
By analyzing subtle cues in voice tone, speech patterns, and text sentiment, these systems will be able to engage in more nuanced and empathetic conversations. This capability will be crucial for handling sensitive customer situations, de-escalating conflicts, and building stronger emotional connections, which can dramatically improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Proactive Hyper-Personalization and Predictive Support
The trend toward personalization will accelerate, moving from reacting to customer behavior to proactively anticipating it. By leveraging advanced predictive analytics, future AI systems will be able to identify a customer’s needs, preferences, or potential problems before the customer even has to articulate them.
This could manifest as an e-commerce site reconfiguring its layout in real time based on a user’s browsing patterns, or a support system proactively reaching out with a solution to a problem it predicts the customer is about to encounter.
This shift creates a truly seamless and supportive experience where the business is always one step ahead.
Interconnected Ecosystems: Bot-to-Bot Communication
The vision for the future includes not just human-to-bot communication, but also bot-to-bot collaboration. In this interconnected ecosystem, different AI systems will be able to communicate with each other to fulfill complex customer requests.
For instance, a customer making a single request to a hotel’s AI assistant to book a room could automatically trigger that bot to communicate with an airline’s bot to book a flight and a car rental service’s bot to arrange transportation, creating a complete travel itinerary from a single point of interaction, all without human intervention.
Integration with Immersive Technologies (AR/VR)
AI will increasingly merge with immersive technologies like Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) to create new forms of customer interaction.
This could include AI-powered avatars providing personalized shopping assistance in a virtual store, an AR overlay guiding a customer through a complex product setup in their own home, or virtual try-ons for clothing and cosmetics. These interactive and engaging experiences will build stronger emotional connections and provide a richer level of service.
These future trends—proactive autonomy, emotional intelligence, and interconnected ecosystems—point toward a single, overarching paradigm shift. The AI of the future will not be a passive tool waiting for a command but an active, autonomous agent working constantly in the background to optimize the customer experience.
However, as AI’s capabilities become more powerful and autonomous, the ethical stakes grow exponentially. An emotionally intelligent AI that can detect a customer’s vulnerability could be used to provide comfort, but it could also be used to exploit that vulnerability for a high-pressure sale.
An agentic AI that can act on a customer’s behalf could be incredibly helpful, but an error could have significant real-world consequences without human oversight.
Therefore, the future of AI is inextricably linked to the future of AI ethics. As these advanced systems are developed, the need for robust ethical governance, radical transparency, and human-in-the-loop accountability frameworks becomes not just important, but absolutely critical to ensuring these powerful technologies are used responsibly and to the ultimate benefit of the customer.
Conclusions
The integration of Artificial Intelligence into customer communication represents a fundamental and irreversible transformation of business operations. The analysis reveals a clear trajectory away from simple, cost-saving automation toward the creation of a comprehensive Intelligent Customer Experience (ICX) that serves as a primary driver of competitive advantage and strategic growth.
Three core conclusions emerge from this report:
The Strategic Imperative is a Synthesized, Hybrid Model. The most effective approach to AI in customer communication is not a choice between technology and people, but a strategic synthesis of both.
AI’s strengths in speed, scalability, and data processing are best applied to routine, high-volume interactions, which liberates human agents to apply their unique skills in empathy, creative problem-solving, and relationship-building to more complex and high-value scenarios.
The success of this hybrid model is critically dependent on the seamless integration and handoff between automated and human channels, a challenge that requires as much focus on workflow design as it does on the AI technology itself.
AI is a Unifying Force that Redefines Organizational Roles. Intelligent communication platforms act as a central nervous system, breaking down the traditional silos between customer service, marketing, and sales. An insight gained in a service interaction can and should immediately inform marketing campaigns and sales strategies.
This interconnectedness necessitates a cross-functional approach to AI strategy and a unified view of customer data. Concurrently, by automating lower-level tasks, AI is systematically elevating the role of the human workforce, demanding a new focus on skills like emotional intelligence and strategic thinking.
Ethical Governance is the Bedrock of Sustainable Success. As AI systems become more autonomous, personalized, and emotionally aware, the ethical considerations surrounding their use become paramount. Issues of data privacy, algorithmic bias, and transparency are not peripheral compliance tasks but central pillars of customer trust.
In an environment where consumers are increasingly conscious of how their data is used and how decisions are made, a demonstrable commitment to responsible AI is no longer just good practice—it is a non-negotiable component of brand reputation and a key differentiator for long-term loyalty.

